ADHD
Everything You Need to Know About ADHD
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a mental health condition that can cause unusual levels of hyperactivity and impulsive behaviors.
People with ADHD may have trouble focusing their attention on a single task or sitting still for long periods of time.
Many people experience inattention and changes in energy levels. For a person with ADHD, this happens more often and to a greater extent compared with people who do not have the condition. It can have a significant effect on their studies, work, relationships, and home life.
Both adults and children can have ADHD. It’s a diagnosis the American Psychiatric Association (APA) recognizes. Learn about types of ADHD and symptoms in both children and adults.
ADHD symptoms
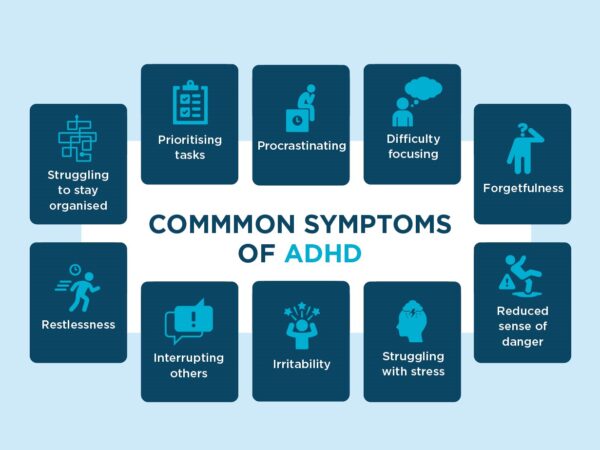
A wide range of behaviors is associated with ADHD. Some of the more common ones include:
having trouble focusing or concentrating on tasks
being forgetful about completing tasks
being easily distracted
having difficulty sitting still
interrupting people while they’re talking
Signs and symptoms can be specific to different aspects of ADHD, such as hyperactivity, impulsivity, or difficulty focusing.
A person who is experiencing hyperactivity and impulsivity may:
find it difficult to sit still or remain seated in class
have trouble playing or carrying out tasks quietly
talk excessively
find it hard to wait their turn
interrupt others when they’re speaking, playing, or carrying out a task
Someone who is having difficulty focusing might:
make frequent mistakes or miss details when studying or working
find it hard to maintain focus when listening, reading, or holding a conversation
have trouble organizing their daily tasks
lose items frequently
be easily distracted by small things happening around them
If you or your child has ADHD, you may have some or all of these symptoms. The symptoms you have will depend on the type of ADHD you have. Explore a list of ADHD symptoms common in children.
-Types of ADHD
To make ADHD diagnoses more consistent, the APA has grouped the condition into three categories, or types. These types are predominantly inattentive, predominantly hyperactivity-impulsive, and a combination of both.
Predominantly inattentive
As the name suggests, people with this type of ADHD have extreme difficulty focusing, finishing tasks, and following instructions.
Experts also think that many children with the inattentive type of ADHD may not receive a proper diagnosis because they don’t tend to disrupt the classroom. ResearchTrusted Source suggests this is more common among girls with ADHD.
Predominantly hyperactive-impulsive type
People with this type of ADHD primarily show hyperactive and impulsive behavior. This can include:
fidgeting
interrupting people while they’re talking
not being able to wait their turn
Although inattention is less of a concern with this type of ADHD, people with predominantly hyperactive-impulsive ADHD may still find it difficult to focus on tasks.
Combined hyperactive-impulsive and inattentive type
This is the most common type of ADHD. People with this combined type of ADHD display both inattentive and hyperactive symptoms. These include an inability to pay attention, a tendency toward impulsiveness, and above-average levels of activity and energy.
The type of ADHD you or your child has will determine the treatment method. The ADHD type you have can change over time, so your treatment may change, too. Learn more about the three types of ADHD.
-What causes ADHD?
Despite how common ADHD is, doctors and researchers still are not sure what causes the condition. It’s believed to have neurological origins. Genetics may also play a role.
ResearchTrusted Source suggests that a reduction in dopamine is a factor in ADHD. Dopamine is a chemical in the brain that helps move signals from one nerve to another. It plays a role in triggering emotional responses and movements.
Other research suggests a structural difference in the brain. Findings indicate that people with ADHD have less gray matter volume. Gray matter includes the brain areas that help with:
speech
self-control
decision-making
muscle control
Researchers are still studying potential causes of ADHD, such as smoking during pregnancy. Find out more about the potential causes and risk factors of ADHD.
-ADHD diagnosis and testing
There’s no single test that can tell if you or your child has ADHD.
A 2017 studyTrusted Source highlighted the benefits of a new test to diagnose adult ADHD, but many clinicians believe an ADHD diagnosis cannot be made based on one test.
To make a diagnosis, a doctor will assess any symptoms you or your child has had over the previous 6 months.
Your doctor will likely gather information from teachers or family members and may use checklists and rating scales to review symptoms. They’ll also do a physical exam to check for other health problems. Learn more about ADHD rating scales and what they can and cannot do.
If you suspect that you or your child has ADHD, talk with a doctor about getting an evaluation. For your child, you can also talk with their school counselor. Schools regularly assess children for conditions that may be affecting their educational performance.
For the assessment, provide your doctor or counselor with notes and observations about your or your child’s behavior.
If they suspect ADHD, they may refer you or your child to an ADHD specialist. Depending on the diagnosis, they may also suggest making an appointment with a psychiatrist or neurologist.
– ADHD treatment
Treatment for ADHD typically includes behavioral therapies, medication, or both.
Types of therapy include psychotherapy or talk therapy. With talk therapy, you or your child will discuss how ADHD affects your life and ways to help you manage it.
Another therapy type is behavioral therapy. This therapy can help you or your child learn how to monitor and manage your behavior.
Medication can also be very helpful when you’re living with ADHD. ADHD medications are designed to affect brain chemicals in a way that enables you to better manage your impulses and actions.
Find out more about treatment options and behavioral interventions that can help ease ADHD symptoms.